What Is GRC in Cybersecurity? A Comprehensive Guide
February 20, 2025
Go back to "News & Updates"

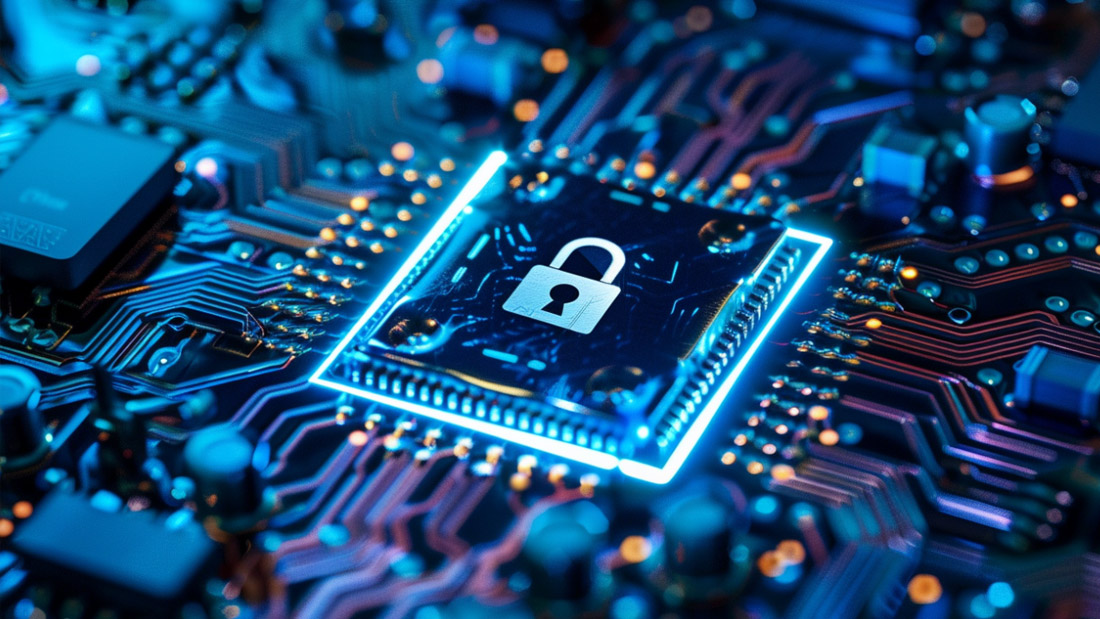
In an era where cyber threats and data breaches are on the rise, organizations need a holistic approach to protect their digital assets. One powerful framework that addresses this need is GRC—Governance, Risk, and Compliance. This blog post from Klipsys Technologies will explore what GRC in cybersecurity entails, why it’s critical for modern businesses, and how your organization can leverage it for robust cyber defenses.
Understanding GRC: Governance, Risk, and Compliance
Governance
Governance refers to the overarching system of policies, procedures, and controls that dictate how an organization’s IT environment is managed. In the context of cybersecurity, governance involves establishing clear responsibilities, objectives, and decision-making processes that align with the company’s strategic goals. By setting the right governance standards, leadership ensures that every department understands its role in maintaining the security and integrity of organizational data.
Risk
Risk management is all about identifying, assessing, and mitigating the potential threats that could harm your company’s information systems. Cyber risks are continually evolving, encompassing issues like hacking, phishing, ransomware, and insider threats. A robust risk management strategy includes regular risk assessments, security audits, and the implementation of controls that can help predict and reduce vulnerabilities.
Compliance
Compliance ensures that an organization meets all relevant laws, regulations, and industry standards regarding data security and privacy. Examples include GDPR, HIPAA, PCI-DSS, and more. Failure to comply with these regulations can result in hefty fines, reputational damage, and legal complications. By maintaining strict compliance protocols, organizations underscore their commitment to data integrity and customer trust.
Why Is GRC Important in Cybersecurity?
- Holistic Security Approach: GRC integrates governance, risk, and compliance efforts, creating a more comprehensive, organization-wide security strategy.
- Reduced Cyber Risks: By performing continuous risk assessments, businesses can prioritize and tackle the most critical vulnerabilities first.
- Regulatory Adherence: GRC processes make it simpler to track and comply with evolving regulations, helping organizations avoid fines and legal issues.
- Enhanced Stakeholder Confidence: Effective GRC practices instill trust among customers, partners, and investors by demonstrating robust data protection measures.
Key Benefits of Implementing GRC in Cybersecurity
- Streamlined Processes: GRC frameworks standardize processes for policy creation, risk assessment, and compliance reporting, ensuring critical tasks are never overlooked.
- Cost-Effective Management: A centralized GRC system helps reduce the expense of managing multiple tools and processes, optimizing resource allocation.
- Transparency and Accountability: Clear documentation and responsibilities make audits straightforward and reveal areas needing improvement.
- Agility and Adaptability: A well-structured GRC system allows organizations to quickly adapt to new threats and compliance mandates.
Common Challenges in GRC Implementation
- Complex Regulations: Global regulations vary, and organizations operating in multiple jurisdictions may struggle to keep up with all relevant laws.
- Resource Constraints: Implementing a GRC framework demands time, expertise, and budget—challenging for smaller teams.
- Lack of Executive Buy-In: Without leadership support, GRC initiatives can fail to gain traction and sufficient resource allocation.
- Technological Silos: Disparate security tools can fragment data and reduce overall visibility, emphasizing the need for a unified GRC platform.
Steps to Implement GRC Effectively
-
1. Assess Your Current State
Begin with a thorough assessment of your existing cybersecurity processes, compliance status, and governance model. Identify strengths, weaknesses, and gaps.
-
2. Define Roles and Responsibilities
Establish who is accountable for different aspects of GRC. Clarity ensures that security tasks are executed consistently and promptly.
-
3. Develop Robust Policies and Procedures
Create policies aligned with both business objectives and regulatory demands. Ensure they are clearly documented and regularly updated.
-
4. Leverage Technology
Invest in GRC tools that provide real-time insights, automate compliance reporting, and streamline risk assessments.
-
5. Train Your Team
Conduct regular workshops and awareness programs so employees remain vigilant about emerging threats and compliance requirements.
-
6. Monitor and Review
GRC is an ongoing process. Regular audits and updates ensure continued relevance and strengthen cybersecurity resilience.
How Klipsys Technologies Can Help
-
GRC Assessments
We conduct comprehensive evaluations of your current practices to identify gaps and opportunities for improvement.
-
Custom GRC Solutions
Our team tailors frameworks to your business size, industry, and regulatory environment for optimized results.
-
Ongoing Support and Training
From employee awareness sessions to regular audits, Klipsys Technologies provides continuous support against emerging threats.
Final Thoughts
In today’s fast-evolving digital landscape, a robust cybersecurity posture is non-negotiable. Governance, Risk, and Compliance (GRC) is a proven methodology that ensures alignment with organizational goals, effective risk mitigation, and strict regulatory adherence. Implementing GRC fosters a culture of security and accountability that resonates throughout your entire organization.
If your business is ready to strengthen its cybersecurity framework, Klipsys Technologies is here to guide you every step of the way. Contact us to learn how we can tailor a GRC solution to help you navigate the complexities of modern cyber threats with confidence.
Ready to Secure Your Future?
Get in touch with Klipsys Technologies today for a comprehensive GRC consultation and discover how we can protect your digital assets against evolving cyber risks.